Joint Research on Application of Antithrombogenic Thermoplastic Elastomer ‘ZELAS AMP’ to Medical Devices
October 8, 2025
Mitsubishi Chemical Corporation (Head Office: Chiyoda-ku, Tokyo; President: Manabu Chikumoto; hereafter ‘MCC’) has initiated a collaborative research project (hereinafter referred to as “the Joint Research”) in partnership with Professor Masaru Tanaka of the Institute for Materials Chemistry and Engineering, Kyushu Univ. (Fukuoka City, Fukuoka Prefecture) and Professor Shigeru Miyagawa of Osaka University Graduate school of medicine, Cardiovascular surgery (Suita City, Osaka Prefecture), focusing on application of our antithrombogenic thermoplastic elastomer ‘ZELAS™ AMP’ to medical devices. Through this Joint Research, MCC aims for market launch of ZELAS™ AMP in 2027 and its global expansion.
In medical devices such as cardiac catheters and cardiopulmonary bypass circuits, anticoagulants have conventionally been coated onto the base resin to prevent blood coagulation and thrombus-related occlusion. However, since the cost of coating processes can only be justified for certain advanced medical devices, there is demand for materials that can provide antithrombogenic properties at a lower cost.
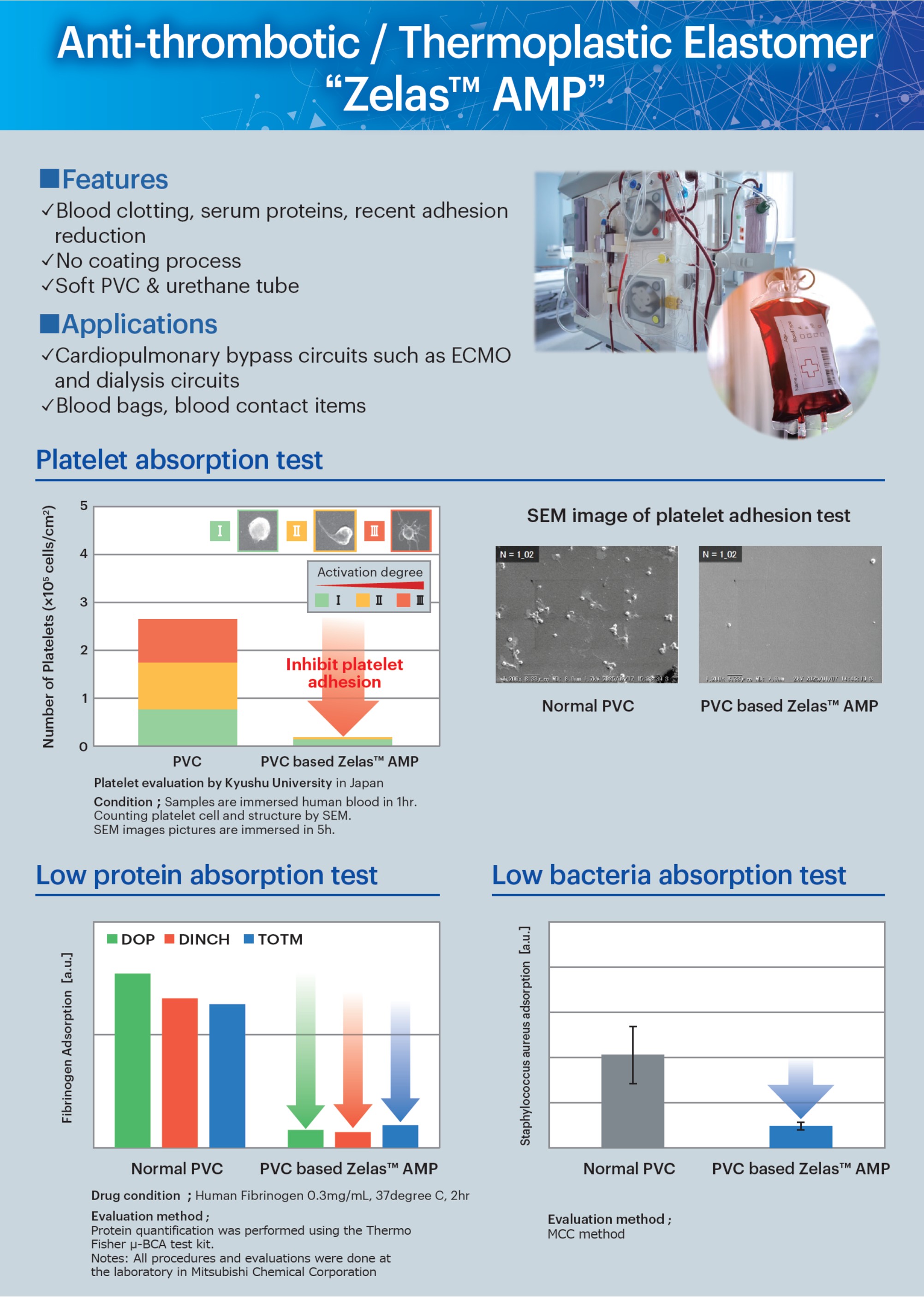
MCC has accumulated advanced formulation and compounding technologies for the medical-grade compound resin ‘ZELAS™ AMP’ over many years and has expanded its global supply system for medical materials※. The key polymer in ZELAS™ AMP is an amphiphilic polymer that combines blood compatibility, derived from its hydrophilic structure, with substrate affinity, derived from its hydrophobic structure. By adding this key polymer of ZELAS™ AMP to resins used as base materials for medical devices (such as polyvinyl chloride, polyurethane, and engineering plastics), antithrombogenic properties, low protein adsorption, and low bacterial adhesion can be imparted to the base material.
The Institute for Materials Chemistry and Engineering, Kyushu Univ. specializes in elucidating material structure and function from the atomic, molecular, and nanoscale to the macroscale, and has particular expertise in the surface design of medical devices. Osaka University Graduate school of medicine, Cardiovascular surgery is a world leader in research and development of advanced medical fields such as heart transplantation, assisted circulation, and regenerative medicine.
In this Joint Research, MCC will pursue the optimal addition and formulation design of ZELAS™ AMP key polymer for various resins used as base materials for medical devices. By developing ZELAS™ AMP in response to the needs of medical professionals, MCC aims to reduce the use of anticoagulants through antithrombogenic properties and eliminate the need for coating processes, thereby lowering risk and manufacturing cost for medical devices that come into direct contact with blood, such as cardiac catheters, cardiopulmonary bypass circuits, and dialysis and transfusion components.
MCC, under its management vision ‘KAITEKI Vision 35’, has designated technology and equipment for new therapeutics as one of its key business domains and aims to support new therapies with high-performance, medical-grade materials. Through the research and development of antithrombogenic thermoplastic elastomer ‘ZELAS™ AMP’ in collaboration with healthcare professionals, MCC will contribute to improving the functionality and safety of blood-contacting medical devices.
【About the Institute for Materials Chemistry and Engineering, Kyushu Univ.】
The Institute for Materials Chemistry and Engineering, Kyushu Univ. engages in a wide range of research, including synthesis of new functional molecules, the chemistry of novel molecular assemblies, the organic-inorganic hybrid materials, and the chemistry related to the application of advanced materials to devices.
Professor Masaru Tanaka is a leading expert in biomedical materials and medical device surface design. In this Joint Research, he will be responsible for evaluating the antithrombogenic properties of various medical materials, including ZELAS™ AMP, and will provide technical advice on nanoscale surface analysis and material design. By leveraging his profound expertise in the creation and application of molecular assemblies and hybrid materials, he will support optimal material design.
【About Osaka University Graduate school of medicine, Cardiovascular surgery】
Osaka University Graduate school of medicine, Cardiovascular surgery has one of the nation’s leading track records in surgical procedures and is at the forefront both domestically and internationally in research and development of advanced medical fields such as heart transplantation, circulatory support, minimally invasive surgery, regenerative medicine, and bio-design. Professor Shigeru Miyagawa is responsible for evaluating biocompatibility and antithrombogenicity using animal models that reflect clinical needs, as well as for conducting verification studies toward practical application. He has established a practical research framework that addresses the diverse requirements of the medical field.
※Acquisition of business from Welset Plast Extrusions Pvt. Ltd in India in 2019
https://www.mcgc.com/english/news_mcc/2018/1204623_7663.html
https://www.mcgc.com/english/news_mcc/2019/1206328_7665.html
Acquisition of business from AdvanSource Biomaterials Corporation in the United States in 2020
https://www.mcgc.com/english/news_mcc/2019/1207875_7665.html
In medical devices such as cardiac catheters and cardiopulmonary bypass circuits, anticoagulants have conventionally been coated onto the base resin to prevent blood coagulation and thrombus-related occlusion. However, since the cost of coating processes can only be justified for certain advanced medical devices, there is demand for materials that can provide antithrombogenic properties at a lower cost.
MCC has accumulated advanced formulation and compounding technologies for the medical-grade compound resin ‘ZELAS™ AMP’ over many years and has expanded its global supply system for medical materials※. The key polymer in ZELAS™ AMP is an amphiphilic polymer that combines blood compatibility, derived from its hydrophilic structure, with substrate affinity, derived from its hydrophobic structure. By adding this key polymer of ZELAS™ AMP to resins used as base materials for medical devices (such as polyvinyl chloride, polyurethane, and engineering plastics), antithrombogenic properties, low protein adsorption, and low bacterial adhesion can be imparted to the base material.
The Institute for Materials Chemistry and Engineering, Kyushu Univ. specializes in elucidating material structure and function from the atomic, molecular, and nanoscale to the macroscale, and has particular expertise in the surface design of medical devices. Osaka University Graduate school of medicine, Cardiovascular surgery is a world leader in research and development of advanced medical fields such as heart transplantation, assisted circulation, and regenerative medicine.
In this Joint Research, MCC will pursue the optimal addition and formulation design of ZELAS™ AMP key polymer for various resins used as base materials for medical devices. By developing ZELAS™ AMP in response to the needs of medical professionals, MCC aims to reduce the use of anticoagulants through antithrombogenic properties and eliminate the need for coating processes, thereby lowering risk and manufacturing cost for medical devices that come into direct contact with blood, such as cardiac catheters, cardiopulmonary bypass circuits, and dialysis and transfusion components.
MCC, under its management vision ‘KAITEKI Vision 35’, has designated technology and equipment for new therapeutics as one of its key business domains and aims to support new therapies with high-performance, medical-grade materials. Through the research and development of antithrombogenic thermoplastic elastomer ‘ZELAS™ AMP’ in collaboration with healthcare professionals, MCC will contribute to improving the functionality and safety of blood-contacting medical devices.
【About the Institute for Materials Chemistry and Engineering, Kyushu Univ.】
The Institute for Materials Chemistry and Engineering, Kyushu Univ. engages in a wide range of research, including synthesis of new functional molecules, the chemistry of novel molecular assemblies, the organic-inorganic hybrid materials, and the chemistry related to the application of advanced materials to devices.
Professor Masaru Tanaka is a leading expert in biomedical materials and medical device surface design. In this Joint Research, he will be responsible for evaluating the antithrombogenic properties of various medical materials, including ZELAS™ AMP, and will provide technical advice on nanoscale surface analysis and material design. By leveraging his profound expertise in the creation and application of molecular assemblies and hybrid materials, he will support optimal material design.
【About Osaka University Graduate school of medicine, Cardiovascular surgery】
Osaka University Graduate school of medicine, Cardiovascular surgery has one of the nation’s leading track records in surgical procedures and is at the forefront both domestically and internationally in research and development of advanced medical fields such as heart transplantation, circulatory support, minimally invasive surgery, regenerative medicine, and bio-design. Professor Shigeru Miyagawa is responsible for evaluating biocompatibility and antithrombogenicity using animal models that reflect clinical needs, as well as for conducting verification studies toward practical application. He has established a practical research framework that addresses the diverse requirements of the medical field.
※Acquisition of business from Welset Plast Extrusions Pvt. Ltd in India in 2019
https://www.mcgc.com/english/news_mcc/2018/1204623_7663.html
https://www.mcgc.com/english/news_mcc/2019/1206328_7665.html
Acquisition of business from AdvanSource Biomaterials Corporation in the United States in 2020
https://www.mcgc.com/english/news_mcc/2019/1207875_7665.html

