Digital Strategy
The Mitsubishi Chemical Group is taking on the challenge of creating value by utilizing digital technologies and digital business models, transforming business processes, and collaborating with other divisions. We will solidify the Group’s competitive advantage as a digital chemical company that can quickly and flexibly adapt to an ever-changing market.
Our Vision to Become a Digital Chemical Company
In view of realizing KAITEKI, the Mitsubishi Chemical Group has defined its vision to become a digital chemical company that can flexibly adapt to continuously changing markets based on a digital strategy that is key to its transformation. We are aiming for global excellence by utilizing digital technologies and digital business models and by transforming processes and how they are managed to improve earnings.
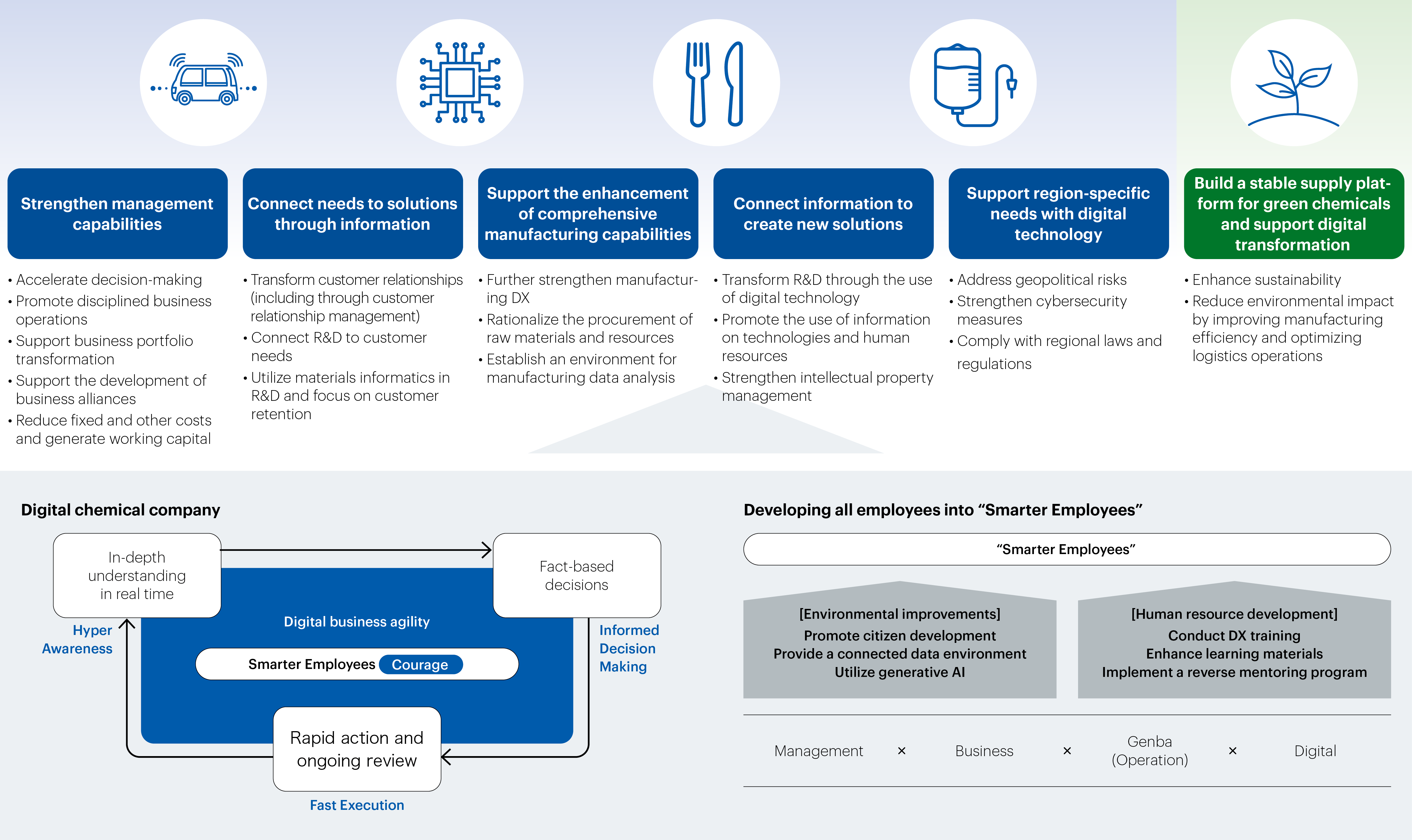
In concrete terms, we will work through a cycle of (1) developing a deep understanding of internal and external environmental changes and customer circumstances in real time (Hyper Awareness), (2) having open discussions and making factually substantiated decisions based on data and information analysis (Informed Decision Making), and (3) springing into action and making improvements through continuous review (Fast Execution).To achieve this, every single employee will need to act with the courage to change conventional ways of thinking and standard business practices. Accordingly, we are creating systems and an environment that allow our employees to be bold and take action.
We do not want our digital divisions to only play a role in developing our IT systems. Rather, we need to shift our attention to working with other divisions to create new value and lead our transformation. To resolve customer issues in a timelier manner, we will utilize digital technology to further facilitate the process of connecting optimal solutions with the needs of society.
To promote business transformation on a global level across the entire Group, we are systematically strengthening collaboration with overseas bases while promoting the standardization of technologies and data. We are gradually integrating our mission-critical systems, and the foundation for advancing business transformation globally is steadily coming to fruition. We aim to continuously evolve as a digital chemical company by drawing on digital technologies to connect and co-create with suppliers, business partners, and customers involved in the advancing digital society, its infrastructure, and our value chains.
To achieve our vision of becoming a digital chemical company, it is imperative that we not only fuel innovation at the operational level through “Genba (Operation) × Digital,” but also multiply value through the broader combination of “Management × Business × Genba (Operation) × Digital.” We will accelerate the transformation of our business processes based on this multiplication in order to create new value.
The Mitsubishi Chemical Group’s strengths lie in its employees who tackle challenges head-on in their day-to-day work. We believe that we can create enormous value by helping every single employee on-site to become a “Smarter Employee” who can utilize digital technologies and digital business models in their work. Through a virtuous cycle of improving educational infrastructure, creating a citizen development environment, and visualizing results, we are enhancing employee motivation and accelerating business and workstyle reforms. Through these efforts, we are transforming a series of business processes.
While promoting strategic improvements that generate immediate results, we are making steady progress in developing the foundations of a digital chemical company (mission-critical system, organization, and human resources) and promoting our digital strategy.
Transforming Businesses Using Digital Technology
Transforming Business Processes and Unifying Business Infrastructure with the Mone System Integration Project
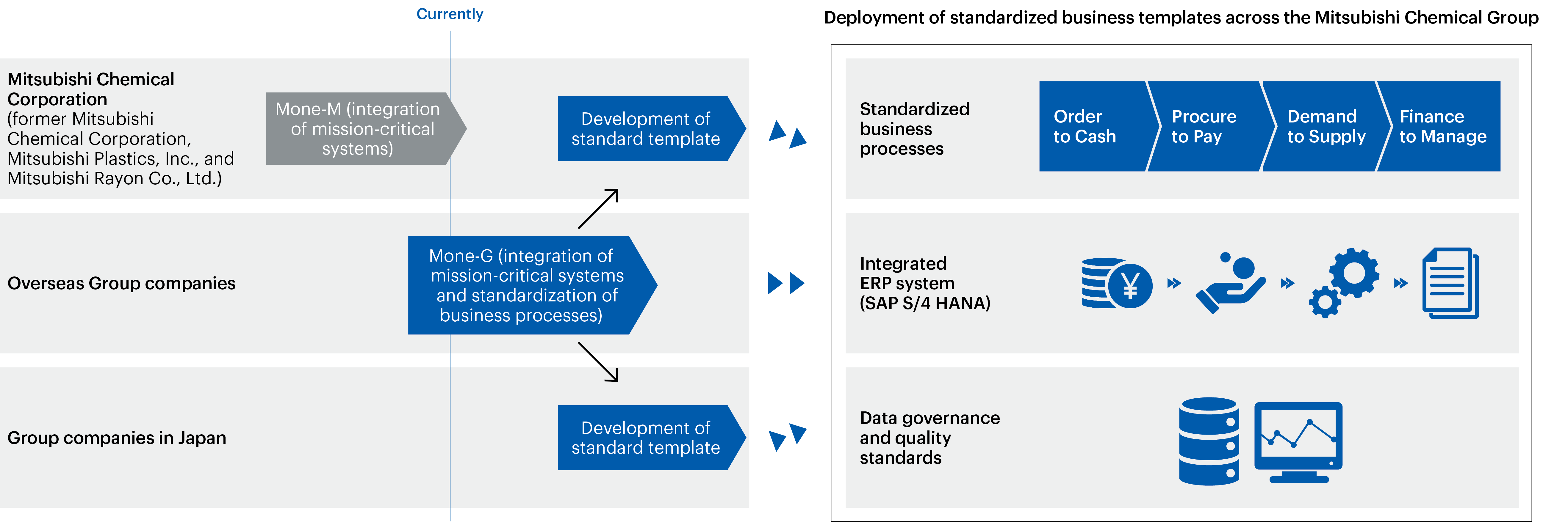
We are developing a global enterprise resource planning system integration project called Mitsubishi Chemical Group one enterprise resource planning (Mone) to standardize mission-critical systems and business processes with the aim of unifying our business infrastructure globally and accelerating business process improvements and value creation.
On April 1, 2025, we began fully operating Mone-M, which integrates the mission-critical systems used in Japan by the former Mitsubishi Chemical Corporation, Mitsubishi Plastics, Inc., and Mitsubishi Rayon Co., Ltd.―the three companies that merged to form the current Mitsubishi Chemical Corporation.
We are also currently rolling out Mone-G, which will unify the mission-critical systems of overseas Group companies and standardize the business processes and data that are based on these systems. In 2024, we implemented Mone-G at four pilot sites and are currently refining and putting the final touches on our business process standardization. This standardization model will be gradually deployed to our overseas bases, with plans to implement it in Japan in the future.
In the past, Group companies used different systems, which led to disparities in business processes and data, making it difficult to manage information consistently and make decisions quickly on a global level. The deployment of Mone is expected to enhance the visualization and use of centralized data across the Group, enabling quicker and more accurate management decisions and stronger cross-departmental collaboration. Furthermore, it will contribute to the optimization of business operations globally through the automation of business processes using the latest technology, reduction of indirect costs, and strengthening of governance.
Promoting Citizen Development Solutions That Accelerate the Transformation of Internal Business Processes in the Age of Generative AI
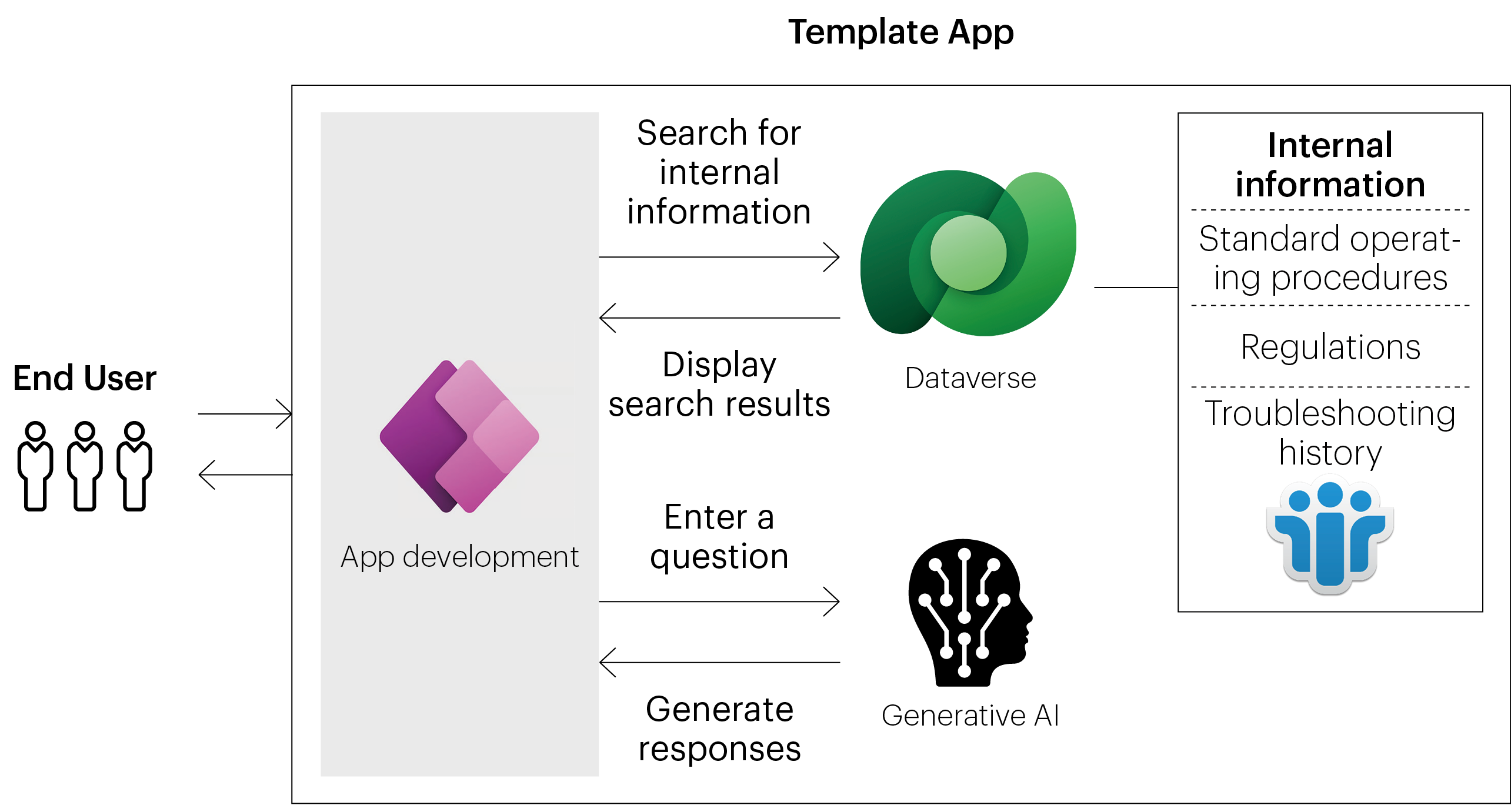
Mitsubishi Chemical Corporation has been promoting the internal use of Microsoft Power Platform to expand the scope of citizen development as a foundation for promoting digital transformation (DX) throughout the company. We have established a new system called Azure OpenAI Integration Hub for Power Platform (OIH) to open up new possibilities for citizen development to quickly and flexibly respond to on-site issues using generative AI.
OIH is an internal service that securely and easily integrates necessary generative AI functions with the systems and applications that run on Microsoft Power Platform. This has made it possible to quickly create a specific environment for the use of AI and incorporate the power of generative AI into business processes even for on-site personnel with no technical knowledge. This innovative environment allows employees to actively develop AI applications, which previously required high knowledge and cost.
What was previously developed individually by IT departments and specialized vendors at considerable cost and effort, can now be developed quickly on-site using standard packages, such as guidebooks and template apps on OIH.
For example, by converting the large amount of standard operating procedures into text, anyone can inquire about the procedures and concepts they would like to know about right away and extract and display the necessary information. A process that took time to search through paper and multiple files for the right information has been streamlined considerably, and new employees as well as those lacking experience can quickly gain access to the same level of knowledge as that of experienced employees. In addition, AI apps with retrieval-augmented generation on operational rules, past equipment problems, near-misses, and past accidents are being introduced one after another, creating new added value from the perspective of improving education, risk alerts, and the efficiency of response to inquiries.
As a “democratic platform” that enables anyone to use generative AI, OIH is becoming the starting point for resolving on-site issues and transforming business processes. Through OIH, Mitsubishi Chemical will work together with its employees to evolve the workplace by promoting DX.
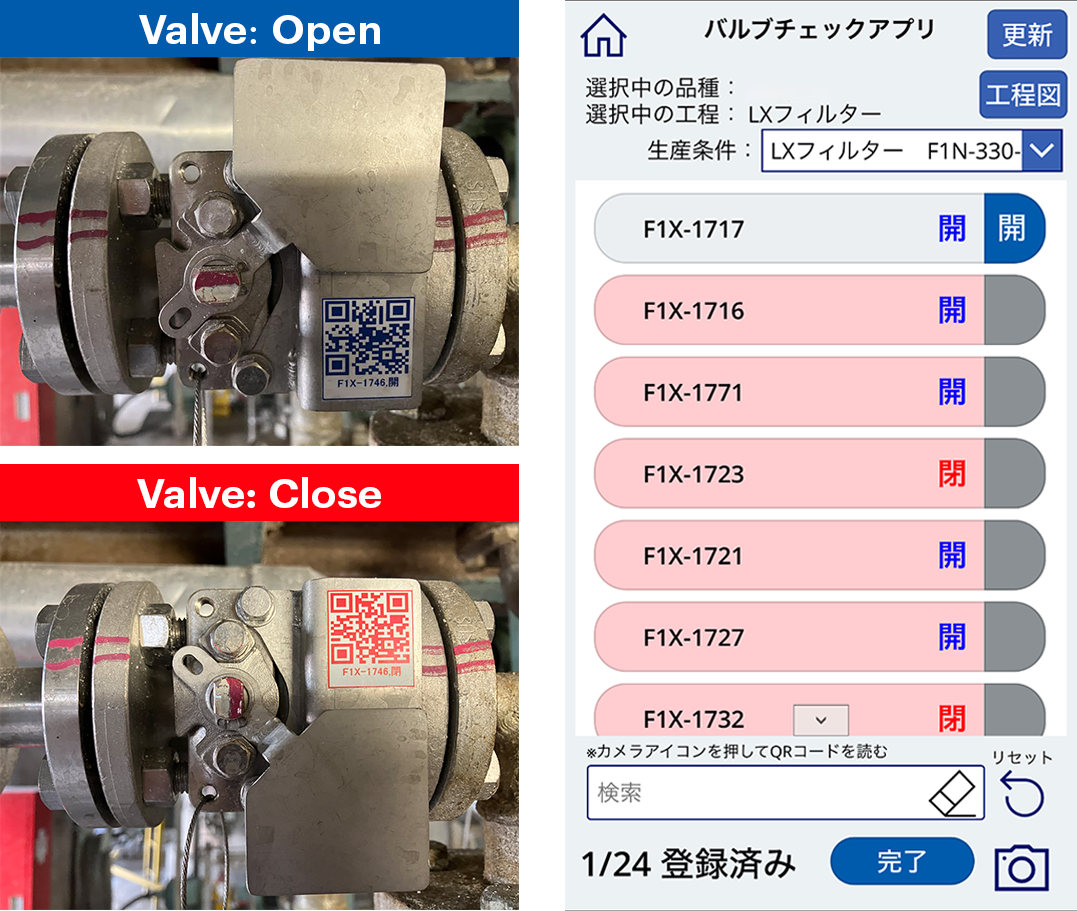
A Valve Check App That Eliminates Startup Issues
Mitsubishi Chemical Corporation’s Hiroshima Plant produces a wide variety of products in small lots, and because production requirements vary by product, the open/close status of more than 100 manual valves must be checked before starting production. In the past, a significant number of checks needed to be made using an extensive checklist of as many as 10 sheets of paper, placing an enormous burden on workers to make sure that everything was in order. Furthermore, even after completing this task, workers had to deal with the psychological burden of worrying about potential problems arising from incomplete checks and other factors. To overcome this situation, we promoted improvements, but were unable to put them into practice due to the large number of valves and the high cost. In the end, to promote citizen development, the Manufacturing Department took the lead in developing a valve check app (electronic checklist) with the help of specialized engineers. By attaching a QR code to each valve and scanning it with a company smartphone, the app enables any worker to check the open/close status without oversight, automatically confirming that the open/close status is consistent with the settings for each task and production requirements. The use of this app has eliminated startup issues and reduced the mental burden on workers.
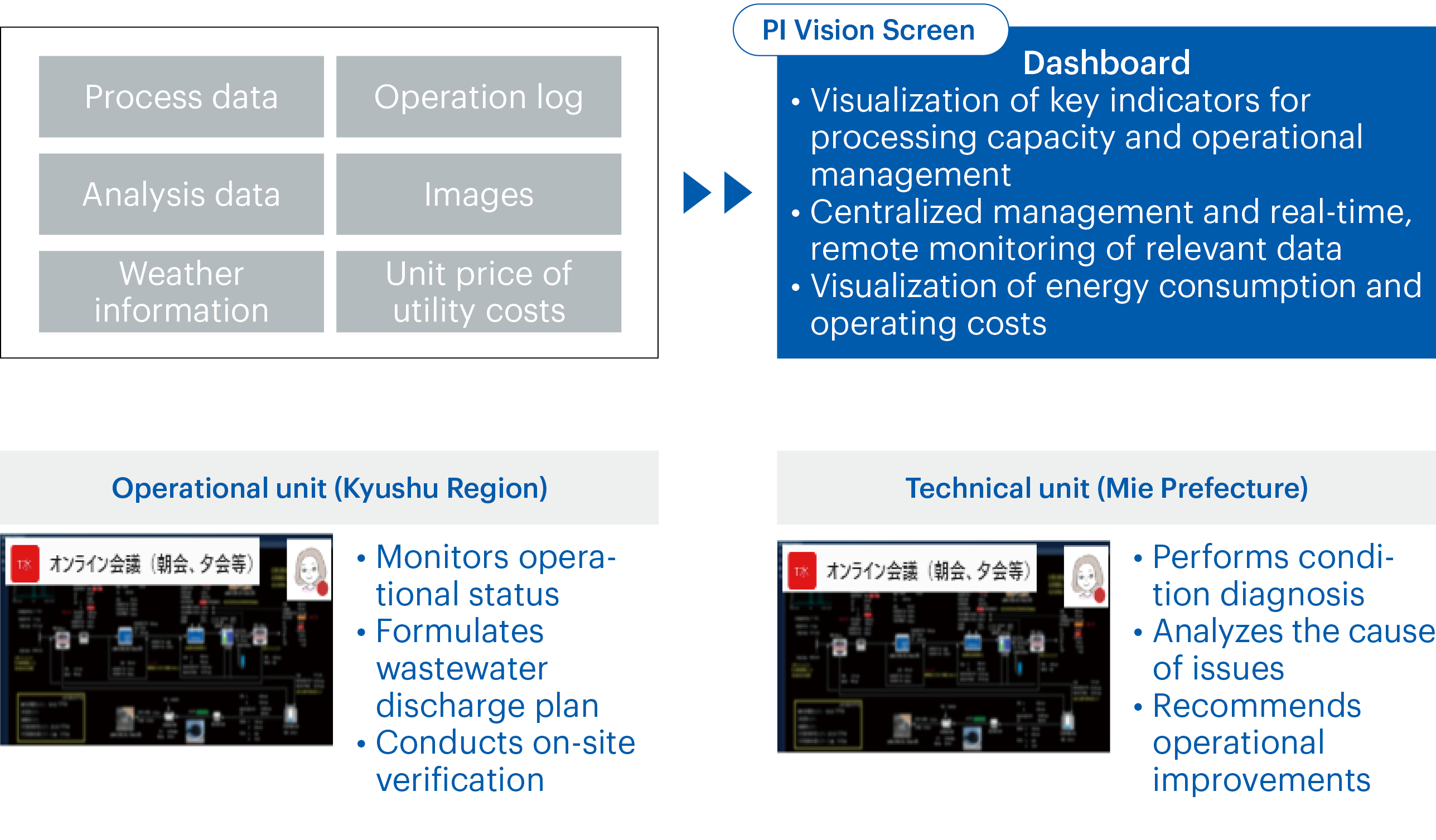
Expanding the Wastewater Treatment Capacity at the Kyushu Plant
Mitsubishi Chemical Corporation’s Kyushu Plant was facing the issue of declining wastewater treatment capacity. In response, we utilized digital technology to optimize the existing systems and review the operating conditions to increase capacity. We first installed the necessary instruments to properly balance organic matter, oxygen, and suspended solids and enhanced our sensing technology. These instruments made it possible to visualize the operational status of the systems and key indicators for operational management, and the visualization of this data on a dashboard has enabled related items to be centrally managed. As a result, it is now possible to monitor treatment capacity remotely and in real time as well as visualize energy usage and running costs.
Until now, the lack of digital technology (sensors) made it difficult to accurately monitor the status of treatment capacity, complicating the process of analyzing the cause of issues. As we had to rely on the experience and intuition of the operator, issues were handled incorrectly at times. By using a dashboard to monitor statuses in real time, we can now respond to and resolve issues quickly using operational data.
Through technical support from remote locations, plants can now receive advice on specific improvement measures, which has enhanced the effectiveness of operations. This has led to improvements in wastewater treatment capacity and operating costs at the Kyushu Plant, which we have designated as a model plant for digital transformation, and we intend to apply similar technologies to wastewater treatment facilities at other sites.
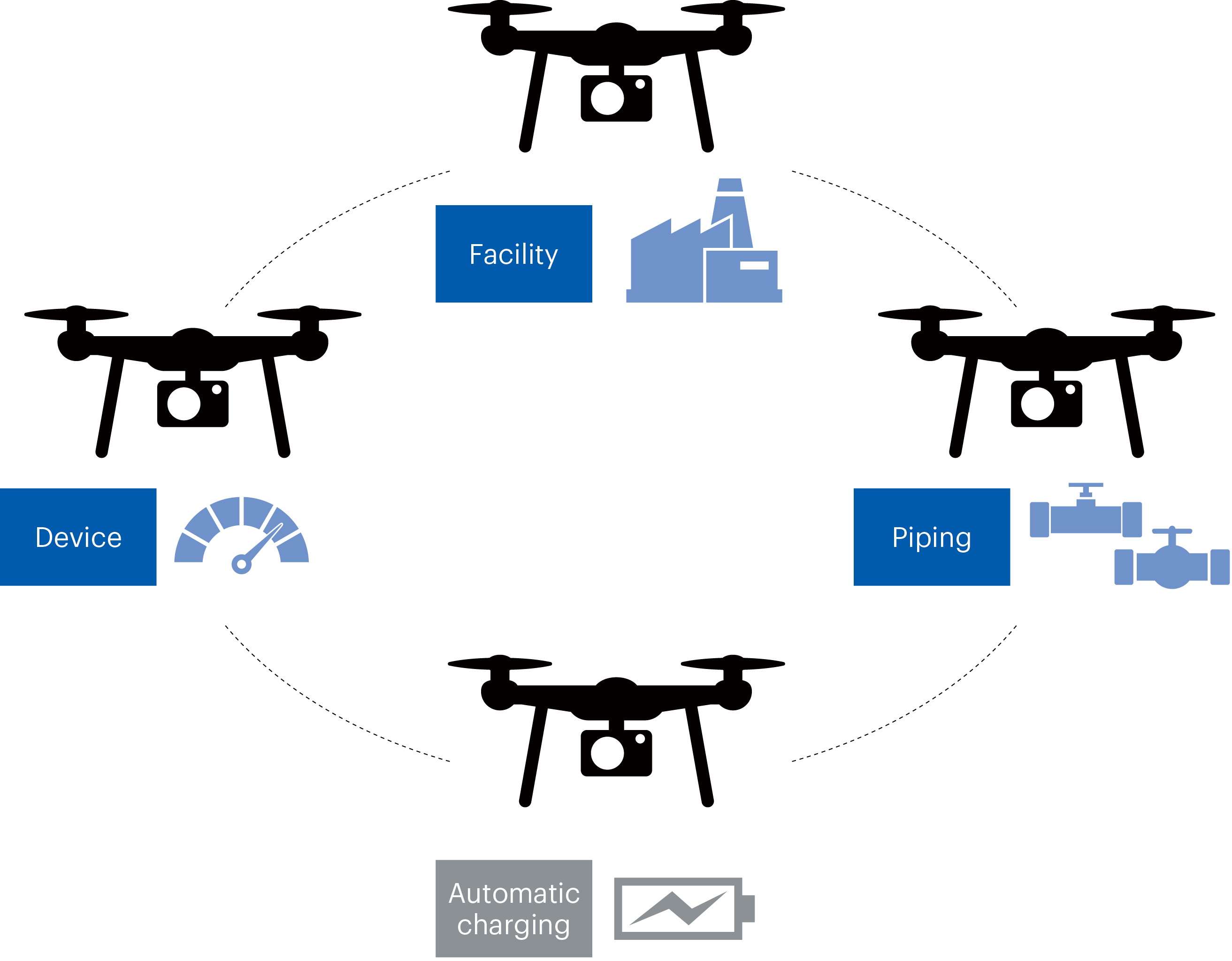
Testing Automated Drone Technology and Promoting the Revision of Firefighting Guidelines in Yokkaichi City
We are working to improve the efficiency and accuracy of daily patrols at the [Yokkaichi Plant / Yokkaichi Industrial Complex] by automating these tasks, which are currently conducted by operators to detect operational and equipment abnormalities at an early stage. As a means to achieve this, Mitsubishi Chemical Corporation’s Tokai Plant carried out technical verification for the automated operation of drones along a predetermined flight route. These kinds of tests are rarely carried out even at the [Yokkaichi Plant / Yokkaichi Industrial Complex] , and therefore we worked closely with the Yokkaichi Fire Department to formulate and execute a test plan and demonstrate the safety and reliability of automated drones, ensuring that they are an effective means for conducting daily patrols in the future.