The Improvement Effects of a Spore-forming Lactic acid producing bacteria Probiotic on Cold-like Symptoms Have Been Demonstrated
June 27, 2024
Mitsubishi Chemical Corporation, a member of the Mitsubishi Chemical Group, performed a clinical study to verify the efficacy of the spore-forming lactic acid producing bacteria probiotic Heyndrickxia(formerly, Weizmannia, bacillus) coagulans (Heyndrickxia coagulans SANK70258)※1 (hereinafter, H. coagulans) for relief of cold-like symptoms in humans and demonstrated that it relieved cold-like symptoms. The study results were published in “Frontiers in Immunology,” dated June 17, 2024※2.
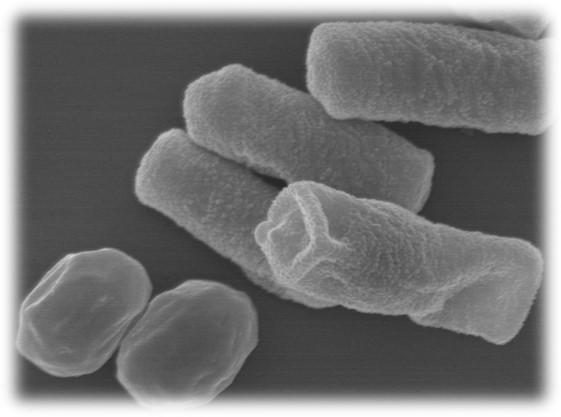
While lactic acid producing bacteria is widely known to have various functions as a useful microorganism, H. coagulans is, unlike other general lactobacillus, characterized by spore formation, which gives it the feature of acid and heat resistance and thereby enables it to reach the intestine alive to germinate and grow there. Previously, we have confirmed its functionalities including its beneficial effects on the intestinal environment, constipation, skin functions, etc. The present clinical study investigated its potential to relieve cold-like symptoms in humans.
The present study was an 8-week intervention study including 79 subjects susceptible to cold-like symptoms aged 20 years or older and younger than 65 years. They were assigned to 2 groups: one receiving a capsule containing at least 1 billion cells of H. coagulans (H. coagulans group: n = 39) and the other receiving a capsule containing no H. coagulans (placebo group: n = 40). Evaluation of cold-like symptoms during the study period revealed significantly lower scores of runny nose, stuffy nose, sneezing, and sore throat as well as significantly fewer cumulative number of days with these symptoms in the H. coagulans group than in the placebo group. These effects in the H. coagulans group were associated with the activation of plasmacyotid dendritic cells (pDC), which are believed to comprehensively control protection from viral infection, and also with the activation of natural killer cells and the increase in salivary secretory IgA level. Furthermore, in the H. coagulans group, inflammation was suppressed with an increase in the intestinal butyric acid level.
These results demonstrated the possibility that H. coagulans activates pDC to elicit comprehensive immunostimulatory effects and enhances butyric acid production in the intestine to suppress excessive inflammatory response, thereby contributing to the relief of cold-like symptoms.
※1 Heyndrickxia coagulans SANK70258
This is a spore-forming lactic acid producing bacteria isolated in 1949 by Prof. Ooki Nakayama (Professor Emeritus of The University of Yamanashi) and has long been used as a probiotic. It is characterized by an ability to reach the intestine alive due to resistance to gastric acid and has been shown to exert various functionalities such as control of intestinal metabolic functions and suppression of intestinal infections.
※2 Information on article:
Title: Heyndrickxia coagulans strain SANK70258 suppresses symptoms of upper respiratory tract infection via immune modulation: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group, comparative study
Authors: Masanori Aida, Naoyuki Togawa, Kazuyuki Mizuyama, Yoshinori Aoki, Shouhei Suehiro, Akiho Sakamoto, Noriyoshi Uchida, Ryouichi Yamada
Journal title: Frontiers in Immunology
https://www.frontiersin.org/journals/immunology/articles/10.3389/fimmu.2024.1389920/full
Information is current as of the date of issue of the individual press release. Please be advised that information may be outdated after that point.

H. coagulans
While lactic acid producing bacteria is widely known to have various functions as a useful microorganism, H. coagulans is, unlike other general lactobacillus, characterized by spore formation, which gives it the feature of acid and heat resistance and thereby enables it to reach the intestine alive to germinate and grow there. Previously, we have confirmed its functionalities including its beneficial effects on the intestinal environment, constipation, skin functions, etc. The present clinical study investigated its potential to relieve cold-like symptoms in humans.
The present study was an 8-week intervention study including 79 subjects susceptible to cold-like symptoms aged 20 years or older and younger than 65 years. They were assigned to 2 groups: one receiving a capsule containing at least 1 billion cells of H. coagulans (H. coagulans group: n = 39) and the other receiving a capsule containing no H. coagulans (placebo group: n = 40). Evaluation of cold-like symptoms during the study period revealed significantly lower scores of runny nose, stuffy nose, sneezing, and sore throat as well as significantly fewer cumulative number of days with these symptoms in the H. coagulans group than in the placebo group. These effects in the H. coagulans group were associated with the activation of plasmacyotid dendritic cells (pDC), which are believed to comprehensively control protection from viral infection, and also with the activation of natural killer cells and the increase in salivary secretory IgA level. Furthermore, in the H. coagulans group, inflammation was suppressed with an increase in the intestinal butyric acid level.
These results demonstrated the possibility that H. coagulans activates pDC to elicit comprehensive immunostimulatory effects and enhances butyric acid production in the intestine to suppress excessive inflammatory response, thereby contributing to the relief of cold-like symptoms.
※1 Heyndrickxia coagulans SANK70258
This is a spore-forming lactic acid producing bacteria isolated in 1949 by Prof. Ooki Nakayama (Professor Emeritus of The University of Yamanashi) and has long been used as a probiotic. It is characterized by an ability to reach the intestine alive due to resistance to gastric acid and has been shown to exert various functionalities such as control of intestinal metabolic functions and suppression of intestinal infections.
※2 Information on article:
Title: Heyndrickxia coagulans strain SANK70258 suppresses symptoms of upper respiratory tract infection via immune modulation: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group, comparative study
Authors: Masanori Aida, Naoyuki Togawa, Kazuyuki Mizuyama, Yoshinori Aoki, Shouhei Suehiro, Akiho Sakamoto, Noriyoshi Uchida, Ryouichi Yamada
Journal title: Frontiers in Immunology
https://www.frontiersin.org/journals/immunology/articles/10.3389/fimmu.2024.1389920/full
Information is current as of the date of issue of the individual press release. Please be advised that information may be outdated after that point.
